Introduction To DAOs
What are DAOs?
Decentralised Autonomous Organisations or DAOs are organisations whose governance and operational activities are often conducted via smart contract interactions on open blockchain platforms. DAOs are commonly made up of people with shared goals who are based all over the world and are often location-agnostic.
There are various types of DAOs, but they all share the common characteristic of being decentralised in how governance is done, meaning that there is no central authority or leader that controls the organisation. Instead, decisions are voted on by the organisation's members with the quorum and majority conditions predetermined in code. This allows for a high degree of transparency and accountability, as well as increased security against fraud and corruption.
Right now, the function of DAOs is predominantly to manage a specific project or application, and they have been used for a wide range of purposes, from developing new open-source software to funding art and journalism.
How do DAOs work?
A portion of a DAO’s operations are run by code, rather than by people. This means that many of the rules that govern the DAO and the mechanisms that operate the organisation are written in code. Therefore, to an extent, the organisation can run itself without the need for a centralised body to drive decision-making and operations.
To do this, DAOs use smart contracts, which are programs that run on blockchains like Ethereum, and provide various functionalities like open and transparent voting, decentralised management of funds and seamless transfer of equity ownership.
The main differentiator between DAOs and traditional organisations is the usage of these smart contracts.
There are various types of standardised smart contracts like governance, multisignature and token contracts that DAOs use to operate and govern themselves.
The basic rules of how a DAO will operate would usually be defined at the time of creation and deployment of a governance contract. These contracts are used in the decision making process of DAOs.
Decisions within a DAO are made through registering votes on these contracts. Members can vote on proposals that are put forward by other members, and the proposal that receives the most votes will be implemented.
In order for a proposal to be put forward, it needs to be approved by a certain percentage of the DAO’s members. This approval threshold is known as the quorum.
DAOs also use multisig (multi-signature) smart contracts to manage their treasuries. Transactions from multisig contracts require 'approvals' from more than one person, often 3 or more, for the transaction to go through.
Token contracts are used by DAOs to create a governance token for themselves which the community members hold in their wallets. The use of tokens allows DAOs to be funded in a transparent and open way as the process is done on a permissionless and transparent financial network.
In order for a DAO to fully function, it needs to have a group of people who are willing to contribute their time, money, expertise or other resources to the organisation. These people are known as the DAO’s contributors, and they each have a certain amount of voting power within the organisation. The level of power that a member has is typically proportional to the amount of money that they have invested in the DAO.
Advantages of DAOs
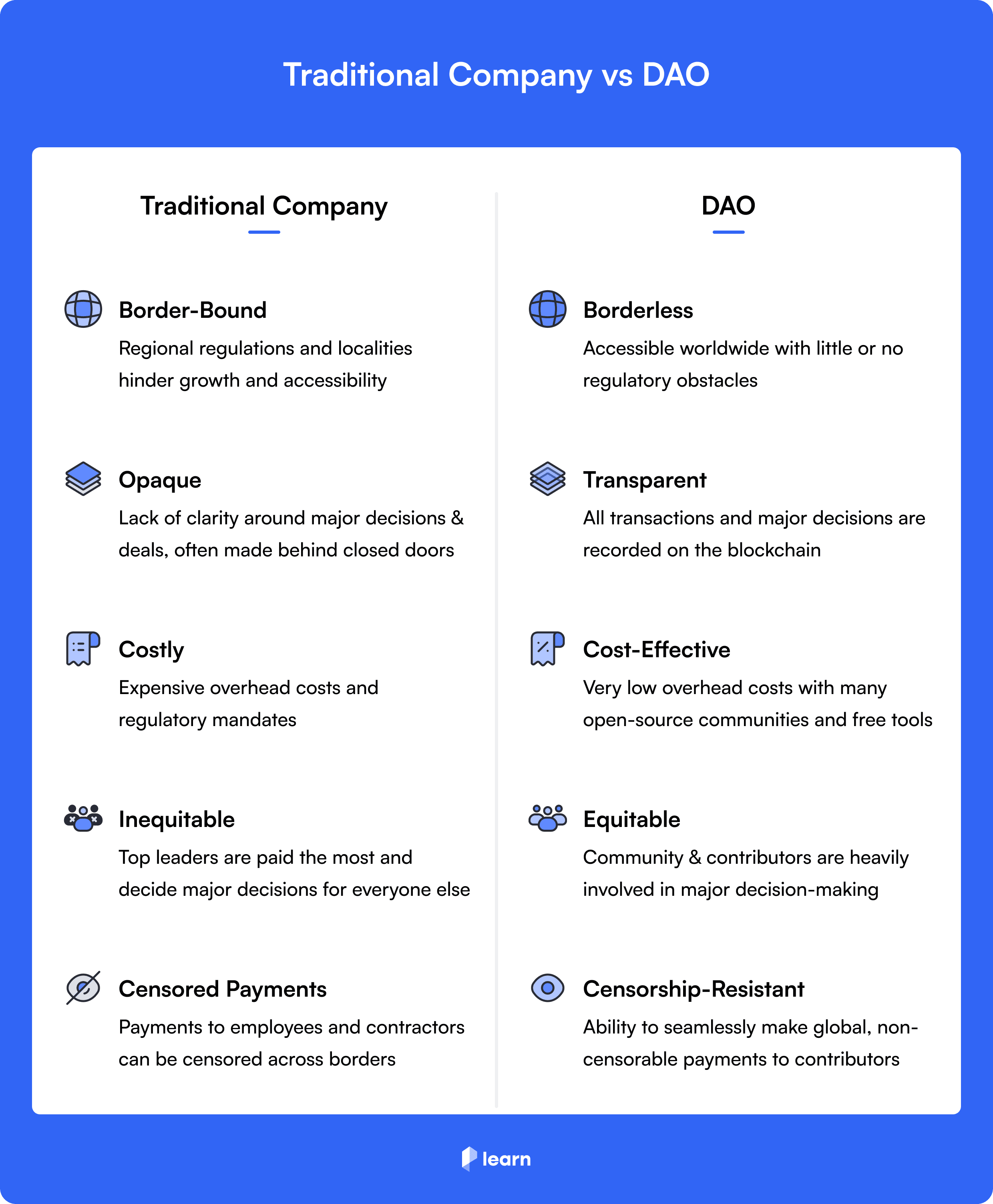
Borderless coordination
It is not easy for internet-native communities to economically coordinate between themselves. So there exists a need for tools that enable these communities to coordinate with each other to achieve shared goals. This boils down to the regulatory hassles and transaction costs that one has to face while making a payment to a person living in another country.
Censorship-resistance
The networks that DAOs are built on are open, borderless and decentralised. Hence, they enable contributors to make non-censorable payments to each other. Contributors at DAOs are also able to work together across borders without facing most restrictions imposed by local regulatory agencies and governments.
Cost-effectiveness
DAOs are often cheaper to run than traditional organisations, as they do not require the same level of infrastructure or overhead costs. This can be attributed to composability between the wide variety of on-chain tools that DAOs use to run their operations.
Transparency
DAOs are transparent, as all transactions and major decisions are recorded on the blockchain. This makes it easy for anyone to see what is happening within the organisation, and makes it more difficult for members to become bad actors.
Equitable
DAOs make use of the wisdom of the crowd by allowing members to vote on proposals. This ensures that the organisation is able to make decisions that are in line with the wishes of its members.
It is possible for every single member of the collective to participate in the governance process. This is a more equitable way of governance that aims to give the power back to every individual who is invested in the organisation.
The Future of DAOs
It has now become easier than ever to set up collectives with a shared goal. Right now, most DAOs are crypto-native. However, we expect this trend to change as DAO tooling gets developed to a point where anyone without the underlying knowledge about crypto infrastructure will be able to create DAOs with a preferred group of people.
DAOs don’t just have to be organisations that are developing a DeFi protocol or an NFT project. Any sort of community can come together and form DAOs. They can be gated communities, non-governmental organisations (NGOs), incorporated firms and governments.
This is a future that all of us at Parcel are working towards by contributing to the cause of making it easy for people to organise themselves.



